Enhancing Clinical Efficiency: Wide Applications of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) in Kidney, Ureter, Bladder (KUB) Imaging
Introduction:
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) has emerged as a versatile and valuable tool in medical settings, offering rapid, non-invasive imaging solutions for a variety of clinical scenarios. In the realm of urology, Kidney, Ureter, Bladder (KUB) imaging is a critical component of patient assessment, and the integration of POCUS has significantly transformed the approach to diagnostics and management.
Applications of POCUS in KUB Imaging:
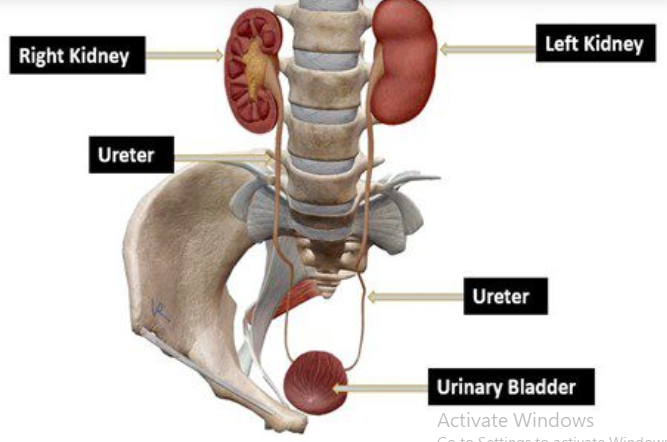
- Renal Assessment: POCUS provides real-time visualization of the kidneys, aiding in the assessment of size, shape, and identifying potential abnormalities such as cysts, tumors, or hydronephrosis. The ability to dynamically evaluate renal structures is particularly advantageous for immediate decision-making.
- Ureteral Imaging: The ureters, responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder, can be effectively visualized using POCUS. Ureteral dilatation, stones, or other obstructions can be identified promptly, allowing for swift intervention and management.
- Bladder Evaluation: POCUS enables quick and accurate assessment of the bladder, helping to identify conditions such as bladder wall thickening, tumors, or calculi. This real-time imaging is especially beneficial for assessing bladder volume and detecting post-void residual urine.
- Renal and Bladder Stones: POCUS is highly sensitive in detecting renal and bladder stones, allowing for immediate identification of size, location, and potential complications. This aids in timely decision-making regarding treatment options, including medical management or surgical intervention.
- Fluid Collections and Infections: POCUS facilitates the detection of fluid collections around the kidneys or in the pelvis, which may be indicative of infections, abscesses, or other pathologies. This information is crucial for guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Clinical Efficiency and Patient Benefits:
- Rapid Diagnosis: POCUS in KUB imaging allows for on-the-spot diagnosis, reducing the time between imaging and decision-making. This is particularly advantageous in emergency and critical care settings.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Compared to traditional imaging modalities such as CT scans, POCUS involves no ionizing radiation. This is especially beneficial for pregnant patients, children, and those requiring repeated assessments.
- Bedside Assessment: The portability of POCUS equipment allows for bedside assessments, enhancing patient comfort and reducing the need for transporting individuals to dedicated imaging facilities.
- Improved Workflow: Integrating POCUS into routine clinical practice streamlines workflow, leading to faster diagnoses and more timely interventions. This ultimately contributes to enhanced patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
The wide applications of Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Kidney, Ureter, Bladder (KUB) imaging have revolutionized the approach to urological diagnostics. By offering rapid, accurate, and radiation-free assessments, POCUS has become an invaluable tool in enhancing clinical efficiency and improving patient care in the realm of urology. As technology continues to advance, the integration of POCUS is likely to play an increasingly pivotal role in the comprehensive management of urological conditions.